How to Install
This section describes how to perform a new installation of Horizon.
Prerequisites
Horizon is built entirely on Kubernetes and has been fully tested on its v1.19.3 ~ v1.24.7 release.
We are assuming you have a basic understanding of what the Kubernetes is and how it runs.
You can use Kind to run a local Kubernetes cluster quickly. Minikube is another highly useful tool to set up a local Kubernetes cluster.
Hardware
The following table lists the minimum and recommended hardware configurations for deploying Horizon.
| Resource | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | 4 CPU | 8 CPU |
| Mem | 8 GB | 16 GB |
| Disk | 40 GB | 80 GB |
Requirements
- Kubernetes cluster version 1.19.3 ~ v1.24.7.
- Installed kubectl command-line tool.
- Have a kubeconfig file (default location is
~/.kube/config). - Installed helm command-line tool.
- Installed ingress-nginx or any other ingress controller.
Installation Process
We use helm to organize Horizon's whole dependencies, which means you can launch a whole system by Helm.
Prepare container runtime
- MacOS
- Linux
setup colima and docker as the container runtime
brew install colima
# Launch Docker runtime by default
colima start --cpu 4 --memory 8
# Or create VM with Rosetta 2 emulation (for MacOS Ventura)
colima start --cpu 4 --memory 8 --vm-type=vz --vz-rosetta
brew install docker
setup docker as the container runtime
apt-get install docker.io
Deploy a kubernetes cluster
Install kind or minikube
- Kind
- Minikube
Linux
# install kind
curl -Lo ./kind https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/dl/v0.11.1/kind-linux-amd64
chmod +x ./kind
mv ./kind /usr/local/bin/kind
MacOS
# install kind
brew install kind
Linux
# install minikube
curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
chmod +x minikube
mv minikube /usr/local/bin/
MacOS
# install minikube
brew install minikube
Run a kubernetes cluster
- Kind
- Minikube
# prepare a kind configuration file `kind.yaml`:
cat <<EOF > kind.yaml
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
kubeadmConfigPatches:
- |
kind: InitConfiguration
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
node-labels: "ingress-ready=true"
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: 80
hostPort: 80
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 443
hostPort: 443
protocol: TCP
EOF
# kubernetes installation, you can specify any k8s version between v1.19.16 and v1.24.7
kind create cluster --image=kindest/node:v1.19.16 --name=horizon --config=kind.yaml
# waiting for the new kubernetes cluster to be running healthily
# install ingress-nginx by helm
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm install my-ingress-nginx -n ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --version 4.1.4 --set controller.hostNetwork=true --set controller.watchIngressWithoutClass=true --create-namespace
- Node in K8s cannot resolve service domain successfully by default, so you need to set serviceIP of
corednsas anameserverin/etc/resolv.conf.
docker exec -it horizon-control-plane bash
echo "nameserver `kubectl get service -n kube-system kube-dns -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterIP}'`" > /etc/resolv.conf
Harborinstalled byHorizonuses an auto-generated tls certificate which will causeX509problem when pulling image on host, so you need to add some contents to the config ofContainerdand restart it.
docker exec -it horizon-control-plane bash
echo '[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.configs."harbor.horizoncd.svc.cluster.local".tls]
insecure_skip_verify = true' >> /etc/containerd/config.toml
systemctl restart containerd
# kubernetes installation, you can specify any k8s version between v1.19.16 and v1.24.7
minikube start --container-runtime=docker --driver=docker --kubernetes-version=v1.19.16 --cpus=4 --memory=8000 --ports=80:80 --ports=443:443
# waiting for the new kubernetes cluster to be running healthily
# install ingress-nginx by helm
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm install my-ingress-nginx -n ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --version 4.1.4 --set controller.hostNetwork=true --set controller.watchIngressWithoutClass=true --create-namespace
- Node in K8s cannot resolve service domain successfully by default, so you need to set serviceIP of
corednsas anameserverin/etc/resolv.conf.
# in host machine
kubectl get service -n kube-system kube-dns -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterIP}' | xargs -I {} docker exec minikube bash -c 'echo "nameserver {}" > /etc/resolv.conf'
Install Horizon by helm
Install Horizon by helm, you can find the latest version of Horizon in Horizon Chart Repo
For users from China, you use values.:
helm install horizon horizon/horizon -n horizoncd --version 2.1.4 --create-namespace -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/horizoncd/helm-charts/main/horizon-cn-values.yaml
helm repo add horizon https://horizoncd.github.io/helm-charts
helm install horizon horizon/horizon -n horizoncd --version 2.1.4 --create-namespace
Keep watching the service status of Horizon. If everything goes well, you can see the following output:
kubectl get pod -nhorizoncd -w
# NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# el-horizon-listener-f5dcd8958-tx675 1/1 Running 0 26m
# horizon-argocd-application-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 39m
# horizon-argocd-repo-server-5c89969bbb-l8hcr 1/1 Running 0 40m
# horizon-argocd-server-579fdbf68c-9p8wr 1/1 Running 0 40m
# horizon-chartmuseum-5db87d9dc8-8j6b9 1/1 Running 4 40m
# horizon-core-64df467d7-jtdl6 1/1 Running 0 24m
# horizon-gitlab-75d5c47c96-zzjpl 1/1 Running 0 17h
# horizon-grafana-78c956d9b6-6th7p 3/3 Running 0 17h
# horizon-harbor-core-86944d7f76-q2lcb 1/1 Running 2 26m
# horizon-harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 39m
# horizon-harbor-jobservice-569559cfd8-c2plt 1/1 Running 2 26m
# horizon-harbor-nginx-7f7cc9b669-64nxz 1/1 Running 0 26m
# horizon-harbor-portal-555876fd5-q9mc5 1/1 Running 0 40m
# horizon-harbor-registry-77977b5d58-64m6l 2/2 Running 0 26m
# horizon-job-bfbc7cb4d-td64p 1/1 Running 0 37m
# horizon-minio-74c84b8c4f-qsdj2 1/1 Running 0 39m
# horizon-minio-provisioning-9tgz8 0/1 Completed 0 26m
# horizon-mysql-0 1/1 Running 0 39m
# horizon-redis-ha-server-0 2/2 Running 0 25m
# horizon-swagger-676fbc8ff9-w8tq7 1/1 Running 0 40m
# horizon-web-5784d89d46-g7bx7 1/1 Running 0 40m
# tekton-dashboard-598fb5b5b7-xmfsz 1/1 Running 0 40m
# tekton-pipelines-controller-688d99f585-kvb58 1/1 Running 0 40m
# tekton-pipelines-webhook-86bd954957-6n7m2 1/1 Running 1 40m
# tekton-triggers-controller-f45c96768-pg8sv 1/1 Running 0 40m
# tekton-triggers-core-interceptors-857dcb75b6-lbprb 1/1 Running 0 40m
# tekton-triggers-webhook-559b5b98cc-c7tmj 1/1 Running 0 40m
Check the installation result
If everything goes well, you can enter Horizon by visiting the url: http://horizon.localtest.me, and you will see the page like below:
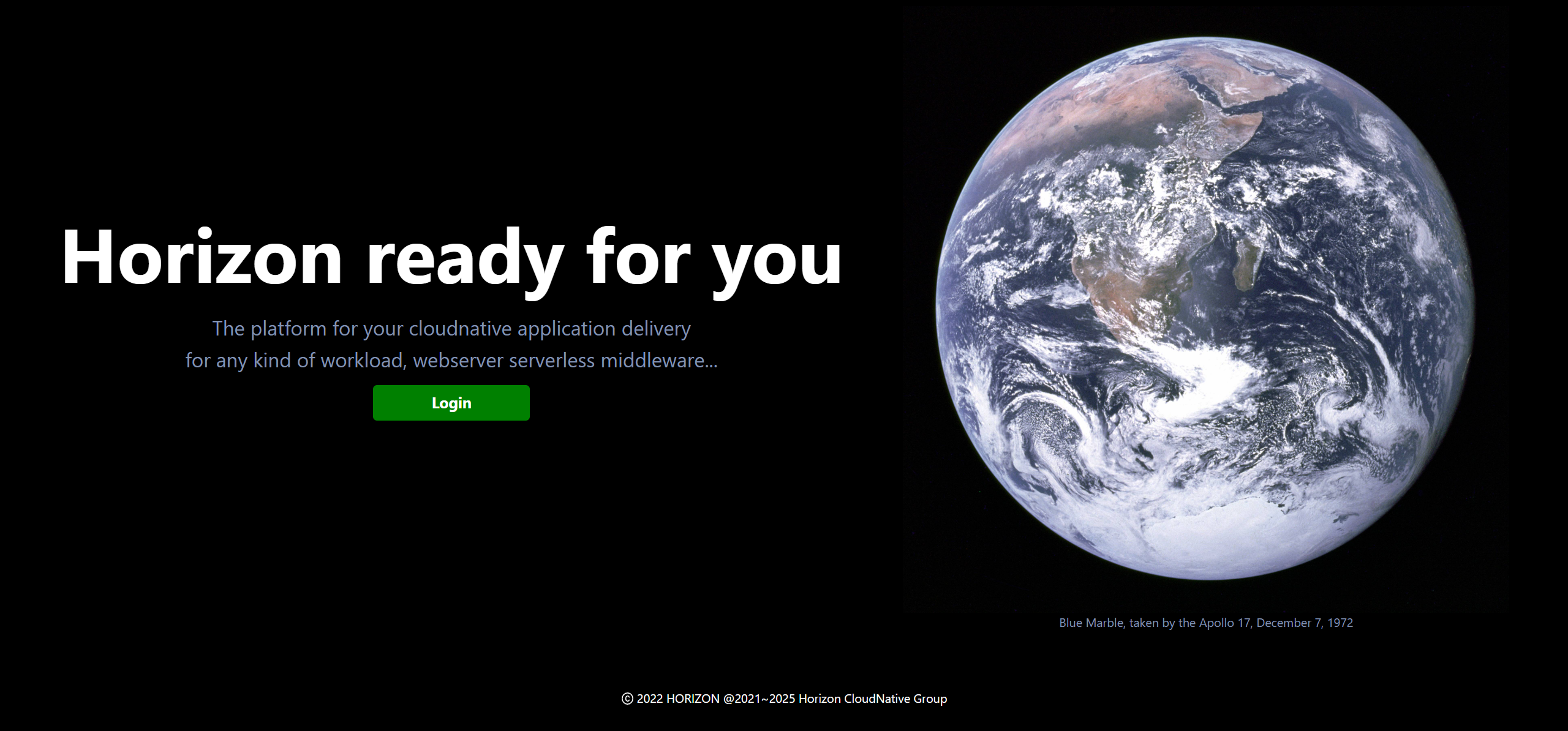
Next, please go to how to deploy your fist workload to experience this amazing system more closely.
Horizon Components
The table below lists the key components that are deployed when you deploy Horizon.
| Component | Version |
|---|---|
| Gitlab | 13.11.7-ce.0 |
| Argo-cd | v2.4.11 |
| Tekton | dashboard: v0.13.0pipeline: v0.28.0triggers: v0.17.0 |
| Chartmuseum | v0.15.0 |
| Grafana | 8.4.6 |
| Minio | 2022.10.29-debian-11-r0 |
| Redis | 6.0.7-alpine |
| Mysql | 8.0.31-debian-11-r0 |